San Rossore Kids
San Rossore kids
San Rossore Kids deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all major pediatric and adolescent diseases.
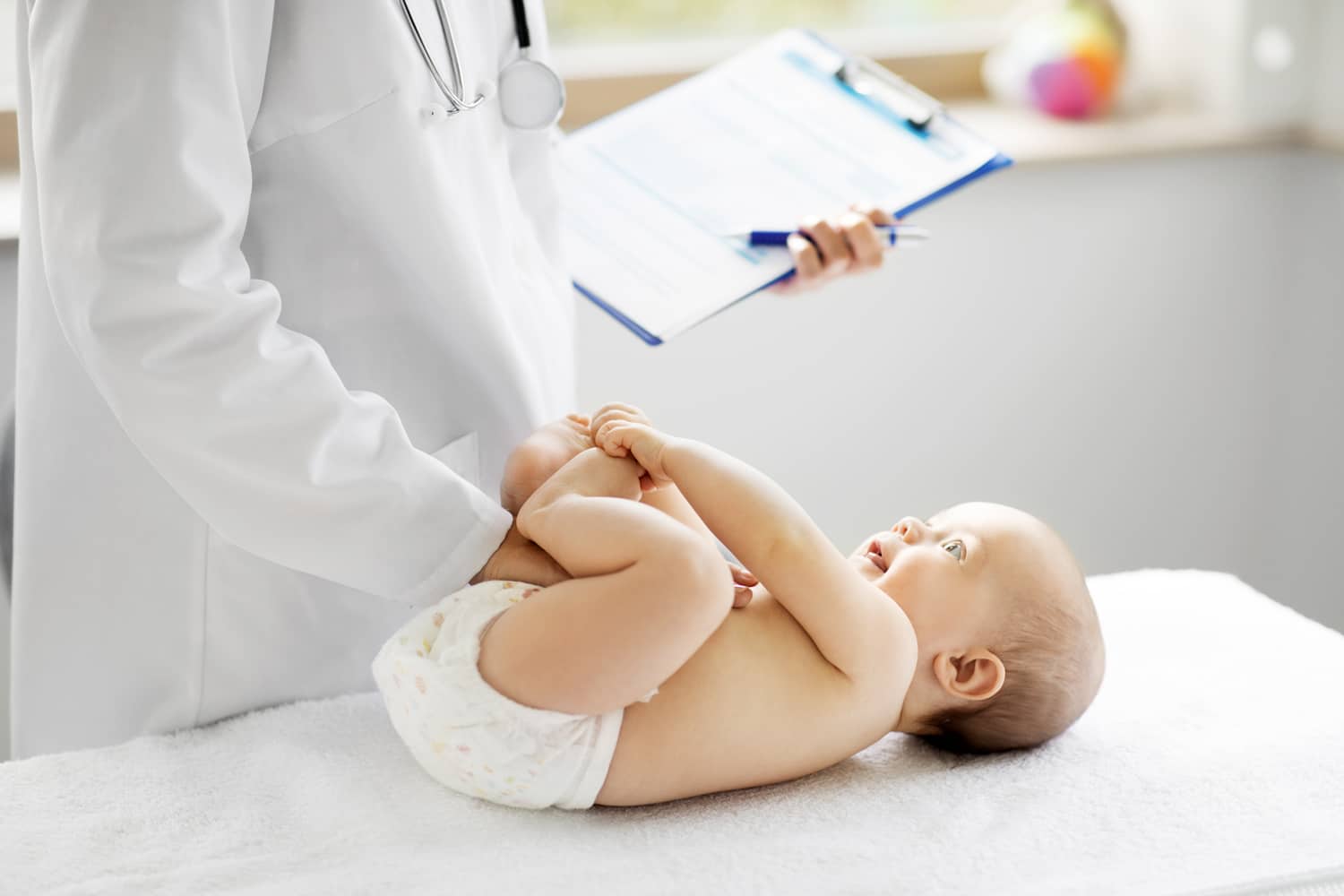

The multidisciplinary approach that characterizes the Casa di Cura San Rossore is also present in the pediatric setting: in fact, the facility provides and supports pediatric physicians who specialize in other fields, specifically ophthalmologists, otolaryngologists, endocrinologists, orthopedics and traumatology, cardiologists, dermatologists, and other key figures such as nutritionists and psychologists.
Thanks to the link with San Rossore Dental Unit, there is also the opportunity to take advantage of dental diagnosis and treatment, delivered through the special Dental Kids program.
At the Casa di Cura San Rossore, young patients will therefore have a multidisciplinary team at their disposal to accompany them and their parents from 0 to 14 years of age, from birth to adolescence.
Paediatrics
Dr. Ilaria Merusi
Ophthalmology
Dr. Anna Cariello
Otolaryngology
Dr. Michele D’Anteo
Dr. Giovanni Segnini
Endocrinology
Dr. Giovanni Gravina
Dermatology
Dr. Dani Hanna
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarifications or other Info please fill out the form below, you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.
San Rossore Eye Unit
San Rossore Eye Unit
The San Rossore Eye Unit at the Casa di Cura San Rossore is among the first in Italy to be equipped with all the most advanced technologies currently on the market and is in fact equipped with state-of-the-art instrumentation that allows all possible visual defects to be treated.
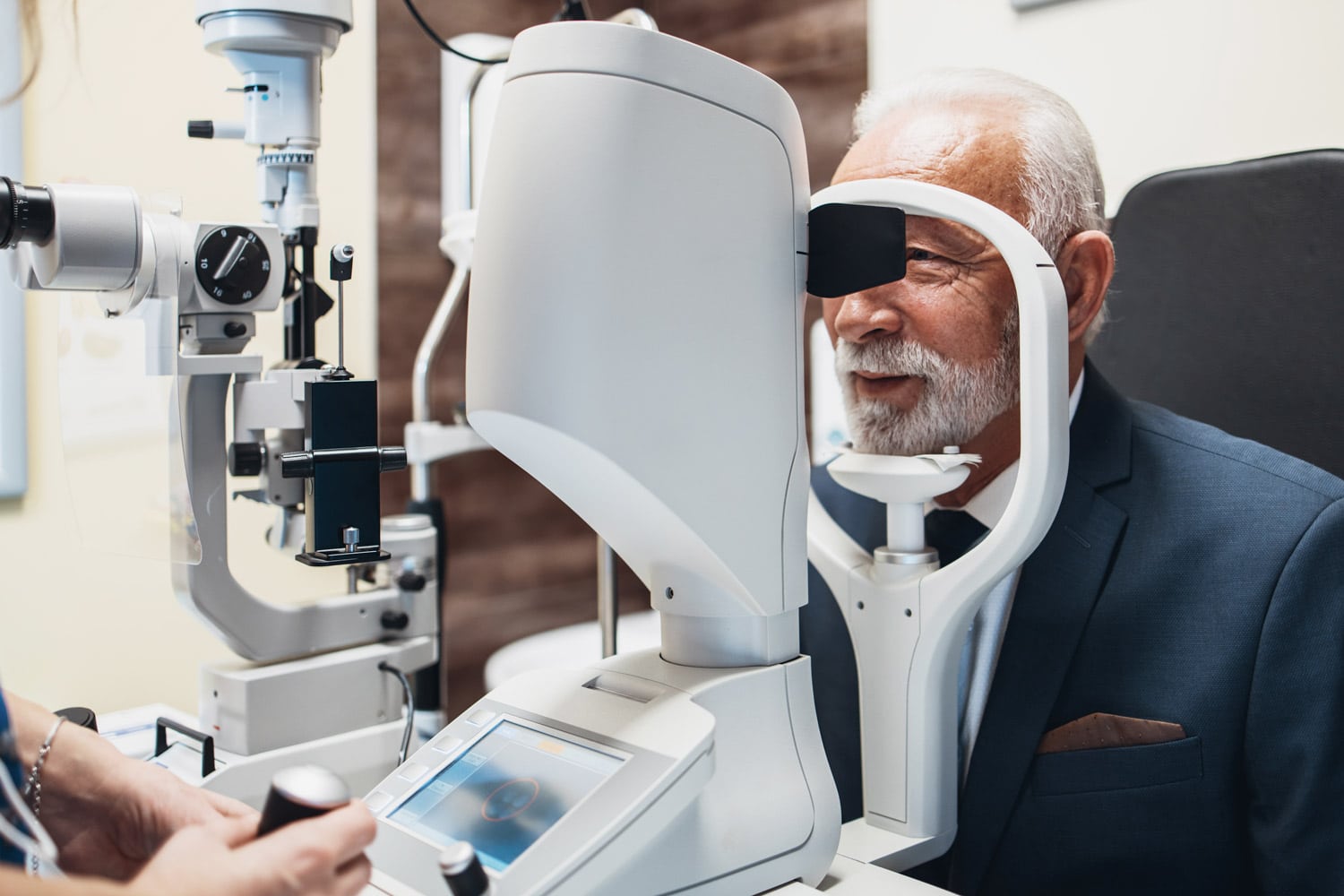
The lasers we have available in our center today are 2:the AMARIS 1050 Hz excimer laser and the VISUMAX 800 femtosecond laser. The choice of which technique to use depends essentially on the clinical characteristics of the individual patient and the type of defect to be corrected; in fact, the technology must be adapted and customized to each patient.
The AMARIS 1050 Hz Excimer Laser represents the highest level of technology on the market today: extremely high treatment precision, maximum reliability and eye-tracker speed, and the ability to perform custom corrections to improve visual performance in eyes that have low visual qualities. This laser is also increasingly being used, in a very select manner, together with cross-linking treatment, for visual rehabilitation in patients with keratoconus.
The VISUMAX 800 femtosecond laser; can be considered to all intents and purposes a kind of light-bulb that in an ultra-precise manner is able to perform super-thin flaps (corneal flaps); combined with the excimer laser it gives rise to the FemtoLasik technique for the treatment of major visual defects: myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, presbyopia.
The procedure for both eyes in the same session takes about 15 minutes, and postoperative discomfort persists for 3-4 hours. Functional visual recovery occurs as early as 12-24 hours, and the recovery time is really fast.
The VISUMAX 800 femtosecond laser is the real novelty in the laser field today, especially for myopia and astigmatism: it consists of the possibility of performing the latest and most modern SMILE refractive technique with the enormous advantage of correcting the defect, weakening the cornea less by going to work in the deepest and weakest part of the cornea itself and preserving the stronger and anterior part, as well as causing less risk of post-laser dryness.
At the San Rossore Eye Unit of the Casa di Cura San Rossore, this method has become the gold-standard for the correction of myopia and astigmatism in all patients, but particularly in sportsmen, in medium to high myopia and in patients with mild dry eye.
The San Rossore Eye Unit of the Casa di Cura San Rossore, where around 2,500 laser operations are performed every year, 1,500 cataract operations of which 70 per cent are carried out using laser-guided robot technology, is the second centre in Italy to have the new VISUMAX 800 laser capable of performing the SMILE technique in 10 seconds and a flap in 7 seconds.
Ophthalmology
Dr. Mammone Massimo
Orthoptics
Dr. Francesco Fortunato
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarifications or other Info please fill out the form below, you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.
Arithmology Center
Arithmology Center
The San Rossore Arrhythmology Center is a unit specializing in the treatment of arrhythmias that aims to offer effective solutions to restore and maintain a normal heart rhythm.

What are arrhythmias:
Cardiac arrhythmias are alterations in the rhythm of the heart, which can manifest as irregular heartbeats that are too fast or too slow. These abnormalities can be caused by several factors, including structural heart disorders, electrolyte imbalances, electrical conduction problems or other medical conditions.
Cardiac arrhythmias can affect the frequency, rhythm, or regularity of heart contractions. In fact, the heart beats normally due to an electrical excitation-conduction system that generates coordinated electrical impulses. These impulses control the rhythm and sequence of contractions of the heart chambers (atria and ventricles), enabling the heart to pump blood effectively.
However, in people with arrhythmias, the heart’s electrical excitation-conduction system may be disturbed, causing abnormal rhythms. Arrhythmias can be classified in several ways, but the two main categories are bradyarrhythmias (slow heartbeat) and tachyarrhythmias (rapid heartbeat).
The bradyarrhythmias include sinus bradycardias and heart blocks, in which electrical impulses are generated or conducted in a slowed manner causing the heart rate to be lower than normal. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, fainting or dizziness.
The tachyarrhythmias include supraventricular tachycardias, atrial flutter and fibrillation, ventricular arrhythmias (ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation). Supraventricular tachycardia is a condition in which an accelerated heart rhythm occurs due to abnormal electrical impulses originating above the ventricles. Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common arrhythmias, characterized by an irregular and fast rhythm in the upper chambers of the heart (atria). Complex ventricular arrhythmias are potentially dangerous arrhythmias in which the heart rhythm can become chaotic and very fast, causing a loss of efficiency in the heart pump.
The causes of cardiac arrhythmias can vary and include preexisting heart diseases such as hypertension, ischemic heart disease, and congenital malformations but can also be caused by electrolyte imbalances, thyroid dysfunction, use of specific drugs, substance abuse, stimulants or alcohol, genetic factors, stress, and anxiety.
The treatment of arrhythmias depends on their severity, associated symptoms and the patient’s health condition. Treatment options may include lifestyle modifications, antiarrhythmic drugs, radiofrequency ablation or cryotherapy, implantation of devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), and in some cases, surgery
The diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias is carried out by Cardiologists who specialize in the management of Cardiac Arrhythmias. The San Rossore Arrhythmology Center is a unit specializing in the treatment of these conditions and aims to offer effective solutions to restore and maintain a normal heart rhythm.
In the Arrhythmology Center, a team of experienced cardiologists focuses on the diagnosis and evaluation of cardiac arrhythmias. Patients undergo a series of specific examinations, such as electrocardiogram (ECG), which records the heart’s electrical activity, echocardiogram, cardiac MRI, and stress test, which are used to identify any underlying structural heart disease, and, last but not least, Holter monitoring to record cardiac activity. As instrumental documentation of arrhythmia remains the key moment of diagnosis, in recent years, new long-term electrocardiographic monitoring systems have been developed and introduced (>24h), which revolutionized the diagnostic pathway of cardiac arrhythmias.
These devices are useful for detecting and recording the heart’s electrical activity for prolonged periods, enabling physicians to obtain a more complete and detailed view of the patient’s heart rhythm, along with related symptomatic correlations. Some of the major long-term electrocardiographic monitoring systems include:
48-72-hour Holter ECG:
The Holter ECG is a portable device that continuously records the electrical activity of the heart over a period of 48-72 hours. The patient wears small electrodes on the chest, which are connected to a portable recorder. During the monitoring period, the patient can carry out normal daily activities. At the end of the recording period, the device is returned to the medical center, where the data are analyzed for arrhythmias or heart rhythm abnormalities.
External Event Recorder:
“External event recorders” are handheld devices that the patient can activate manually when experiencing symptoms or episodes of arrhythmia. When a symptom occurs, the patient presses a button on the device, which records the heart’s electrical activity for a short period, usually several minutes to several hours. These devices are useful for capturing sporadic events or transient symptoms that might not be recorded by other monitoring modalities. The same recording can be made with a portable ECG with durations typically as short as 30 seconds, which, via special apps can be emailed as a pdf to the referring physician for timely diagnosis.
External Loop Recorder:
“External loop recorders” are devices similar to “event recorders,” but are capable of continuously recording the heart’s electrical activity for a longer period of time, often up to 30 days. These devices are used to monitor patients with less frequent arrhythmias or intermittent symptoms.
Internal Loop Recorder:
“Internal loop recorders,” also known as implantable loop recorders, are smaller devices that are surgically implanted into the subcutaneous tissue. These devices can continuously monitor the heart’s electrical activity for longer periods of time than external loop recorders, often up to 3 years or more. Data can be transmitted to physicians remotely via wireless connection.
The use of these new long-term monitoring systems has enabled physicians to more accurately diagnose and treat arrhythmias, improving the clinical management of patients and enabling more personalized treatment pathways. These devices are particularly useful for patients with intermittent symptoms or arrhythmias that are difficult to detect with conventional diagnostic techniques.
Finally, in selected cases in which the clinical diagnosis remains uncertain, additional invasive tests, such as endocavitary electrophysiological study, may be necessary to obtain an accurate diagnosis and plan the appropriate treatment.
Correct electrocardiographic documentation of clinical arrhythmia is critical to planning appropriate treatment. The San Rossore Arrhythmology Center is a unit specializing in ultraspecialty diagnostics of cardiac arrhythmias.
The Arrhythmology Center offers a wide range of pathways and therapeutic treatments for cardiac arrhythmias. After a comprehensive evaluation, the team of specialists develops an individualized treatment plan for each patient, taking into account the severity of arrhythmias, symptoms and individual health conditions. Available treatment options include:
Drug therapy: specific drugs are prescribed to control and regulate heart rhythm, thereby reducing the frequency and intensity of arrhythmias.
Electrical cardioversion: a procedure in which a controlled electrical discharge is applied to the heart to restore a normal heart rhythm.
Catheter ablation: a minimally invasive procedure in which one or more catheters are inserted into veins or arteries and guided to the heart to destroy the cells responsible for arrhythmia.
Implantation of cardiac devices: In some cases, it may be necessary to implant a pacemaker or cardiac defibrillator to monitor and correct the heart rhythm.
Regarding implantable electrical devices, alongside traditional “transvenous” (using leads introduced through a central vein such as the subclavian), new technologies have been introduced in recent years, such as “leadless” pacemakers and subcutaneous defibrillators.
The pacemaker leadless are implantable devices that are placed directly into the heart, without the need for traditional electrodes (leads). These miniaturized, capsule-sized devices are inserted through a minimally invasive procedure, usually through a catheter that is inserted into the femoral vein and guided to the heart. The absence of traditional leads minimizes the risk of complications associated with such devices, such as infection or catheter malfunction.
The Subcutaneous defibrillators are implantable devices designed to monitor the electrical activity of the heart and provide an electrical discharge when a severe arrhythmia, such as ventricular fibrillation, is detected. Unlike conventional defibrillators, which are implanted internally and require electrodes passing through the veins to the heart, subcutaneous defibrillators are placed entirely under the patient’s skin, in the left lateral region of the chest. This approach reduces the risk of complications associated with intravascular electrodes and simplifies the implantation procedure.
All of these devices, which are regularly available and implanted at the Casa di Cura San Rossore, represent important innovations in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, offering safer and more convenient solutions for patients. Of course, the choice of the most appropriate therapeutic device will depend on the assessment of the medical specialist, taking into account the patient’s individual characteristics and specific clinical needs.
As part of the radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, electroanatomical mapping systems and zero-beam techniques have revolutionized the therapeutic approach, providing physicians with more precise and effective tools to identify and treat the areas responsible for arrhythmias.
The electroanatomical mapping systems allow physicians to obtain a detailed three-dimensional representation of the heart and its electrical structures during the ablation procedure and to create real-time maps of the heart’s electrical activities. During ablation, physicians can use these maps to accurately identify the problem areas responsible for arrhythmias and guide catheters in a targeted manner to apply radiofrequency to the areas to be treated. The use of electroanatomic mapping systems has greatly improved the accuracy and effectiveness of ablations, reducing the risk of complications, increasing the success rate of treatments, and
minimizing traditional radiological exposure during the procedure. Indeed, the adoption of zero-ray techniques has helped to improve the safety of surgeries and reduce X-ray exposure for patients and operators.
The combined use of electroanatomic mapping systems and zero-ray techniques is a priority of the San Rossore Clinic. These approaches enable clinicians to more accurately identify the sources of arrhythmias, optimize the ablation strategy, and achieve a higher rate of therapeutic success, while ensuring maximum safety for patients and operators.
What are the most common symptoms of cardiac arrhythmias?
Symptoms of cardiac arrhythmias can vary from person to person, but the most common include palpitations (feeling of an irregular or accelerated heartbeat), feeling of the heart missing or stopping, dizziness, fatigue, dyspnea (difficulty breathing) and fainting. However, some arrhythmias may be asymptomatic and are often discovered during routine examinations.
What are the main causes of arrhythmias?
Cardiac arrhythmias can be caused by a variety of factors, including structural heart disease, such as ischemic heart disease, heart failure or cardiomyopathy, electrolyte imbalances (such as low potassium or magnesium levels), thyroid dysfunction, drug or alcohol abuse, excessive caffeine consumption, stress and anxiety. In some cases, arrhythmias may be hereditary.
Are cardiac arrhythmias dangerous?
The severity of cardiac arrhythmias varies greatly. Some arrhythmias are harmless and require no treatment, while others can be dangerous and require immediate intervention. It is important to consult a physician for accurate evaluation and proper management of arrhythmias. Some arrhythmias can increase the risk of complications, such as heart failure or stroke, if not treated properly.
What are the risk factors for the development of arrhythmias?
Risk factors for the development of cardiac arrhythmias include advanced age, the presence of pre-existing heart disease, such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, smoking, alcohol or drug abuse, stress and anxiety, a family history of cardiac arrhythmias or inherited heart disease, imbalanced electrolytes, and taking certain medications.
How can I prevent cardiac arrhythmias?
Although it is not always possible to completely prevent cardiac arrhythmias, some measures can help reduce the risk of developing them. These include adopting a healthy lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol and caffeine consumption. It is also important to manage stress effectively and control underlying health conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes, through proper medical care.
What is an event recorder?
The event recorder is a portable device that records the electrical activity of the heart for extended periods, usually several weeks to several months.
What is an event recorder for?
The event recorder is useful for capturing occasional episodes of arrhythmias that might go undetected during brief monitoring. Patients can manually activate the event recorder when they experience symptoms of arrhythmia, allowing physicians to analyze the recorded events and make an accurate diagnosis.
What is the Portable ECG?
It is a portable medical device designed to monitor the electrical activity of the heart. It is a type of single- or multi-lead ECG (electrocardiogram) that allows users to record their heart activity via a mobile application.
How does the Portable ECG work?
The Portable ECG works by connecting the device to a phone or tablet via a sensor or electrode. The user holds the device in the hands or rests it on the chest for a few seconds, and records the electrical activity of the heart. The data are then displayed on the mobile application and can be shared with a health professional for analysis.
Why should I use the Portable ECG?
The Portable ECG can be used to record the ECG of the heart easily and conveniently in a wide variety of situations, especially on occasions of suspicious symptoms (e.g., heart palpitation) that are rare and of short duration, such that recording by traditional instruments (e.g., ECg op ECG Holter-24h) is not possible . It can be useful to monitor the electrical activity of the heart at home and to check the effectiveness of certain cardiac treatments. The device enables users to have more control over their heart health and share data with health professionals for accurate assessment.
Can I share the recorded data with my doctor?
Answer: Yes, the data recorded with can be shared with your doctor or a health professional. Kardia’s mobile application allows reports to be generated that can be sent via e-mail or other means of communication. Sharing data with a physician can provide important information for accurate assessment of cardiac health.
What is a loop recorder?
The loop recorder is a subcutaneous implantable device that continuously records the electrical activity of the heart for an extended period of time.
What is a loop recorder for?
The loop recorder is particularly useful for patients who present with sporadic episodes or unclear symptoms of arrhythmia. The device continuously records electrical activity, enabling physicians to detect and analyze arrhythmic events over time for accurate diagnosis.
What is an electrophysiological (EP) study?
Electrophysiological study is an invasive procedure in which catheters are inserted through veins to record the electrical activity of the heart and stimulate specific cardiac regions.
What is the purpose of an electrophysiological study?
Electrophysiological study is useful for identifying the origin and cause of arrhythmias, assessing response to antiarrhythmics, and guiding therapeutic decisions, such as radiofrequency ablation.
What is a subcutaneous ICD?
The subcutaneous ICD is an implantable device that continuously monitors heart rhythm and provides an electrical discharge to interrupt dangerous arrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation.
What are the indications for subcutaneous ICD implantation?
Implantation of a subcutaneous ICD is recommended for patients at high risk of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, such as those with a history of sudden cardiac arrest or impaired ventricular function.
What is a leadless pacemaker?
The leadless pacemaker is an implantable device that stimulates the heart to maintain a regular heart rhythm, without the need for traditional (lead) leads.
What is ablation of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias?
Ablation of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to disrupt the abnormal circuits in the heart’s electrical conduction system responsible for the tachycardias.
How is ablation of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias performed?
During ablation, catheters are inserted into the vascular system and guided to the heart. Using dedicated energy, an injury is created or the tissue that causes tachycardias is destroyed. This prevents the passage of abnormal electrical impulses and restores normal heart rhythm.
What are the benefits of ablation of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias?
Ablation can reduce or completely eliminate episodes of tachycardia, thus improving the patient’s quality of life. In addition, it can reduce or eliminate the need for long-term antiarrhythmic drugs.
What is atrial fibrillation ablation?
Atrial fibrillation ablation is a procedure that aims to interrupt or control the chaotic electrical activity in the upper chambers of the heart (atria) responsible for atrial fibrillation.
How is atrial fibrillation ablation performed?
During ablation, catheters are inserted into the vascular system and guided to the heart. Through the use of dedicated energy, an injury is created or heart tissue is blocked that contributes to atrial fibrillation. This helps restore a regular heart rhythm.
What are the benefits of atrial fibrillation ablation?
Ablation can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of atrial fibrillation episodes, improving the patient’s quality of life. In some cases, it can completely eliminate the need for antiarrhythmic drugs. Ablation may also reduce the risk of stroke associated with uncontrolled atrial fibrillation.
Please note that these answers are general and each individual may have unique situations. It is always advisable to consult a medical specialist for personal evaluation
Head of Interventional Cardiology
Dr. Maria Grazia Bongiorni
Interventional Arithmology
Dr. Andrea Di Cori
Dr. Antonio Canu
Dr. Mario Giannotti
Dr. Matteo Parollo
Clinical Arithmology
Dr. Valentina Barletta
Dr. Sara Sbragi
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarifications or other Info please fill out the form below, you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.
Vascular Center
Vascular Center
The Vascular Center was born within the Casa di Cura San Rossore in 2009 with the intention of organizing a complex and multifaceted activity, carried out until then by several Specialists independently.
The Center has a comprehensive focus on the Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of all Vascular Pathologies.
He received the following awards :
- European Reference Center for Training in Phlebology from the UEMS (European Union of Medical Specialists)
- Certification as an Advanced Phlebology Center by the Italian Society of Phlebology
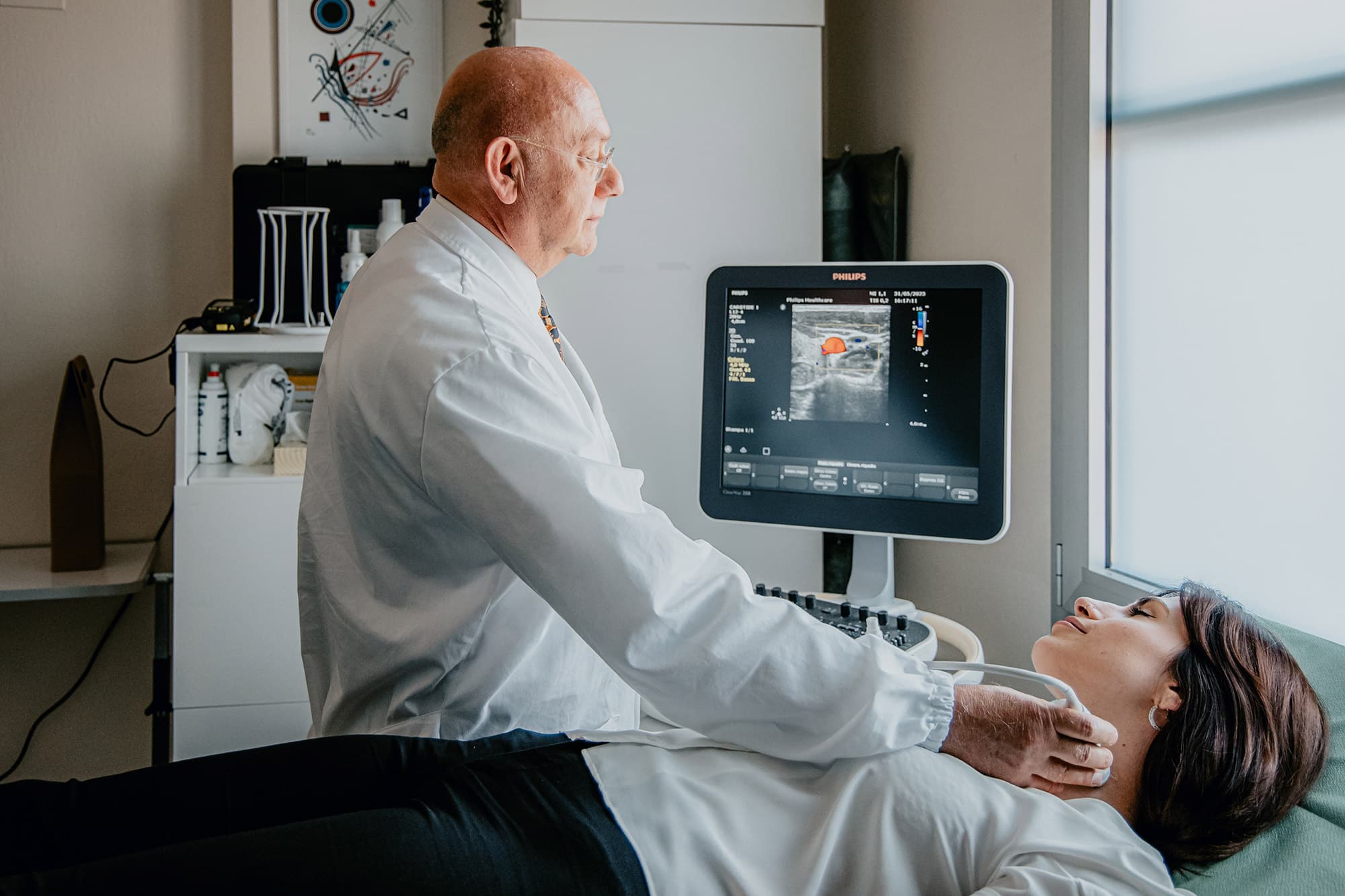
Executable examinations:
- Specialist examination vascular surgery
- Specialist examination angiology
- Specialist phlebology examination
- Echocolordoppler examination cerebroafferent vessels (carotid, vertebral)
- Arterial and venous echocolordoppler examination of the lower limbs
- Arterial and venous echocolordoppler examination of the upper limbs
- Echocolordoppler examination of abdominal vessels (aorta and iliac vessels, cava and iliac veins)
- Echocolordoppler examination of renal and visceral arteries
- Saliva (DNA) tests for cardiovascular risk assessment and thrombophilia
- Assessments of vascular malformations
- Diagnosis and treatment of deep and superficial venous thrombosis
- Sclerotherapy of capillaries, reticular veins, varices
- Lower extremity varices with minimally invasive techniques (lkaser, radiofrequency, sclerotherapy, CHIVA) on an outpatient basis and under local anesthesia
- Mechanical lymphatic drainage (or pressotherapy) for edema or phlebolymphedema
- Elastocompressive bandages
- Treatment of ulcers and skin injuries in general (decubitus, phlebostatic, lymphatic, arteriopathic ulcers)
- Heterologous skin grafts
- Small amputations in patients with diabetic foot
- Incision and drainage of hematomas
- Lower limb varices with the following techniques
- Stripping
- Laser or radiofrequency
- CHIVA
- Sclerotherapy and scleromousse
- Simple phlebectomies
- Interventions for hemorrhoidal goiters with HELP Laser technique;
- Incision and drainage of thrombosed hematomas and varicose goiters
- Placement of central venous catheters (PIC, PORT etc)
- Placement of caval fiilters (in the prevention/treatment of thromboembolism )
- Peripheral angioplasties in arteriopathic patients
- Major and minor lower limb amputations
- Treatment of vascular malformations
Vascular surgery
Dr. Roberto Di Mitri – Head of the Vascular Center, Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Vascular Diseases and specialist in Vascular Surgery
Dr. Vasiliki Kamargianni – Specialist in Vascular Surgery
Phlebology
Dr. Costanza Martelli
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarifications or other Info please fill out the form below, you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.
To access clinics and for reservations contact the Dedicated Secretariat at +39 050 586430
Breast Unit
Breast Unit
A Breast Unit is a multidisciplinary center composed of professionals who specialize in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of breast pathology. This model of care allows for therapeutic planning that achieves the best possible outcomes.

It is scientifically proven that women treated by a dedicated multidisciplinary team receive personalized care with higher cure rates. The Breast Unit consists of an integrated group of specialists dedicated to the treatment of breast cancer who have all the resources needed to provide a high-quality care pathway.
Breast Unit specialists also work to improve the quality of life of patients undergoing treatment.
In our Breast Unit, it is easy to find qualified referring physicians, schedule visits and examinations quickly, and minimize sources of anxiety and waiting times.
The Breast Unit at Casa di Cura San Rossore offers:
- Integrated pathway between the various disciplines involved in the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer;
- Innovative surgical techniques, especially from a plastic reconstructive point of view;
- Cutting-edge medical therapies;
- Specialized diagnostic evaluation using innovative tools;
- Highly qualified multidisciplinary team: radiologist, pathologist, anesthesiologist, breast surgeon, reconstructive plastic surgeon, nuclear physician, medical oncologist, radiation oncologist, physical therapist, psycho-oncologist, nurse.
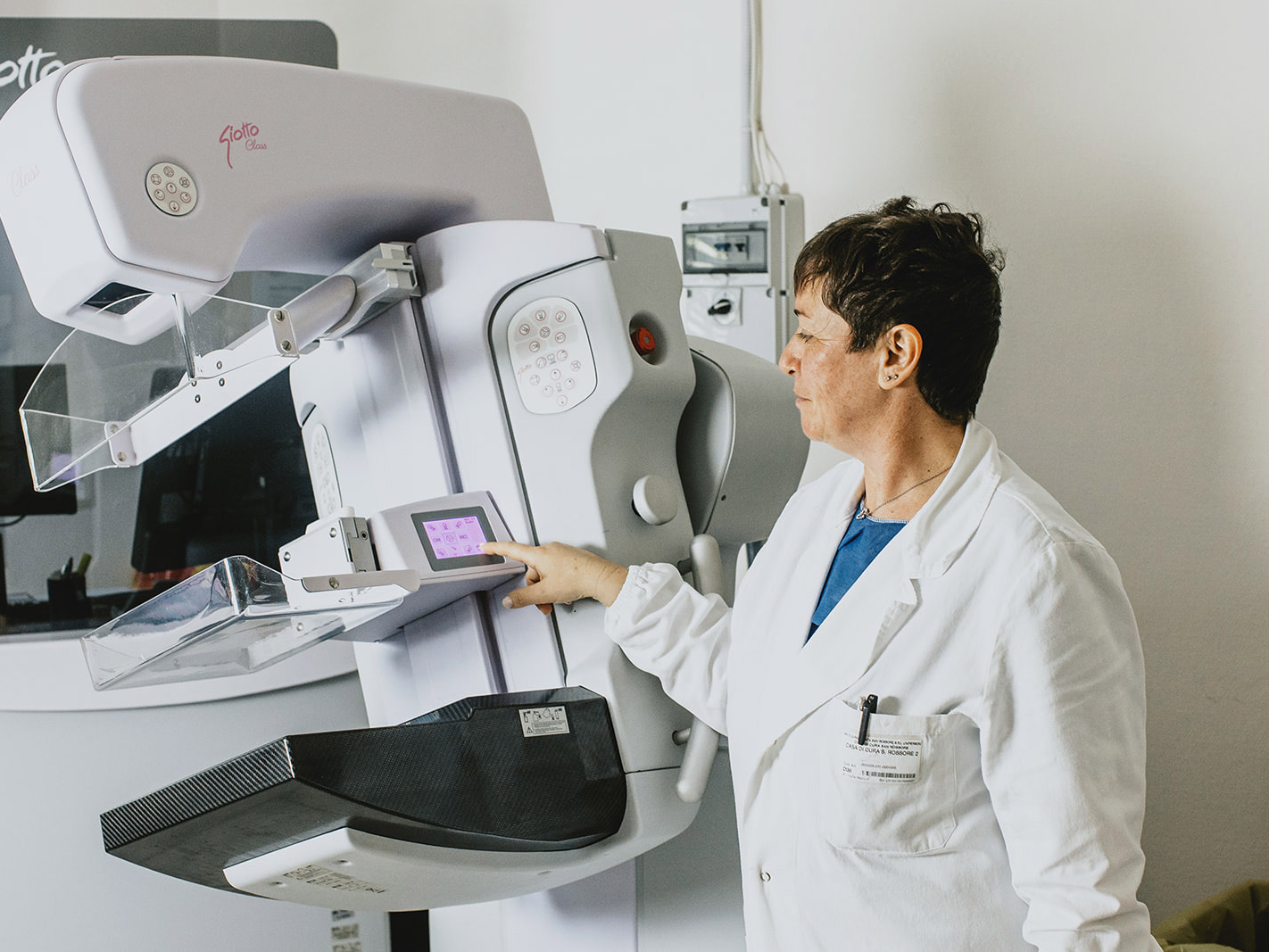
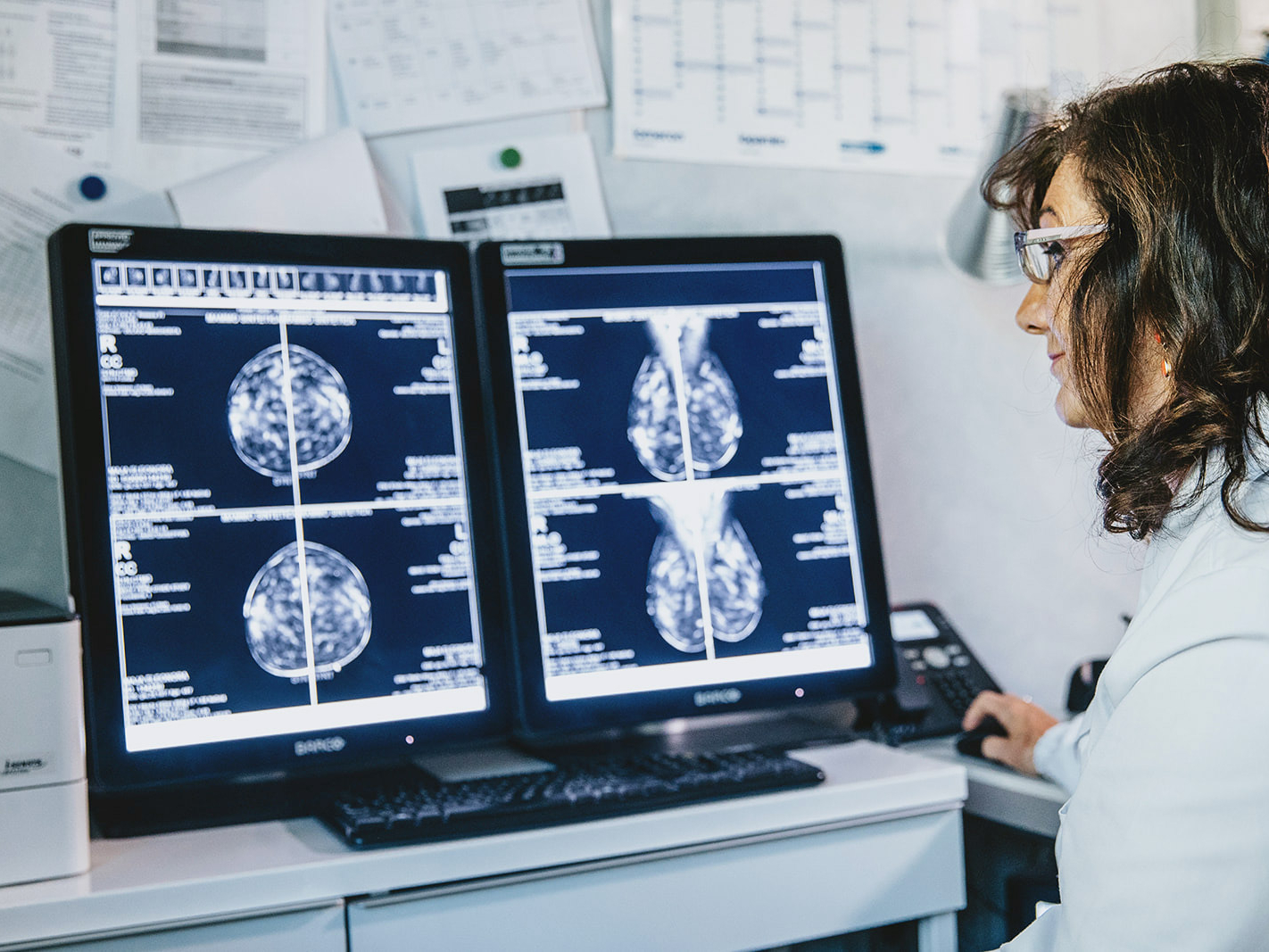
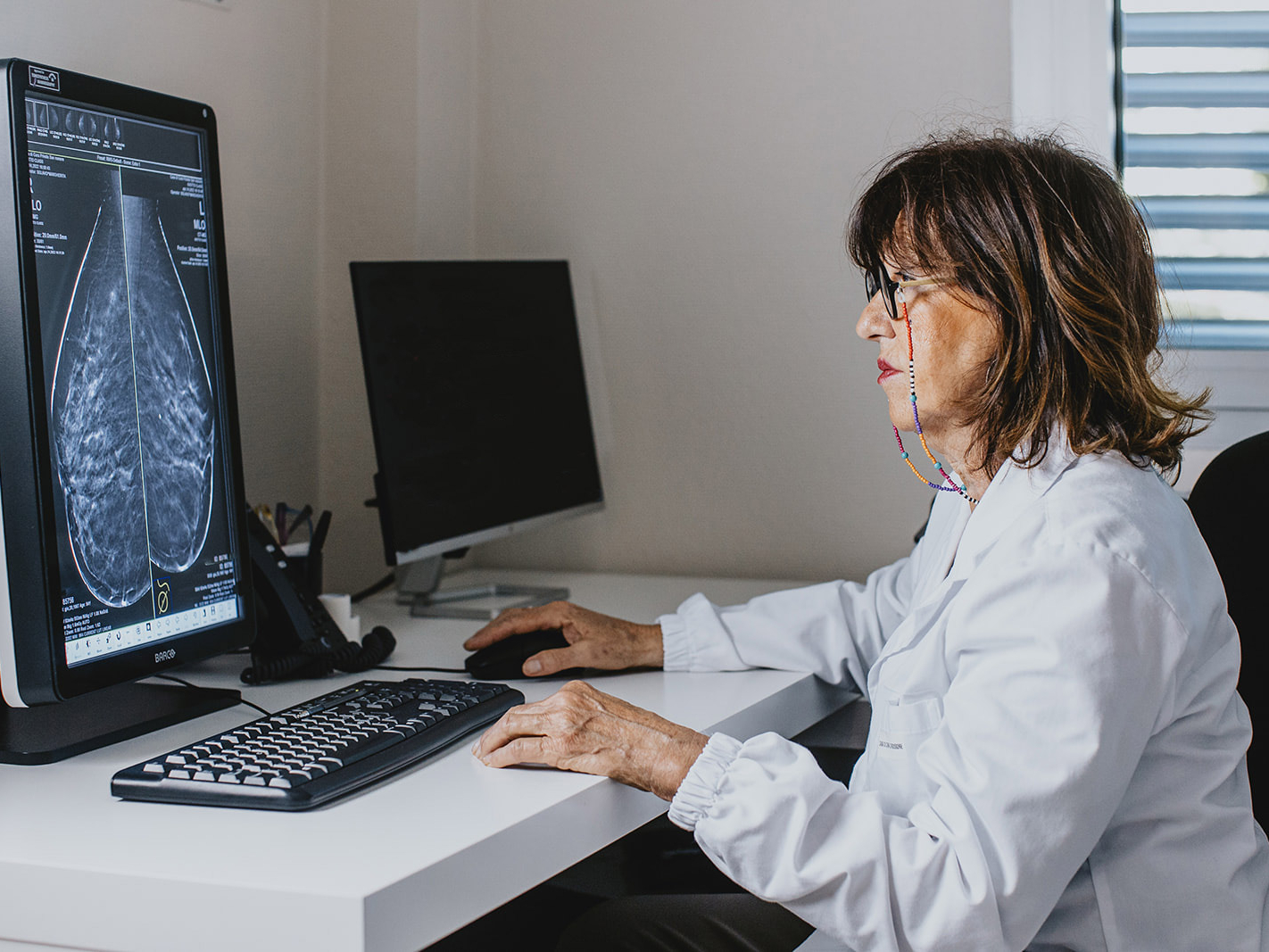
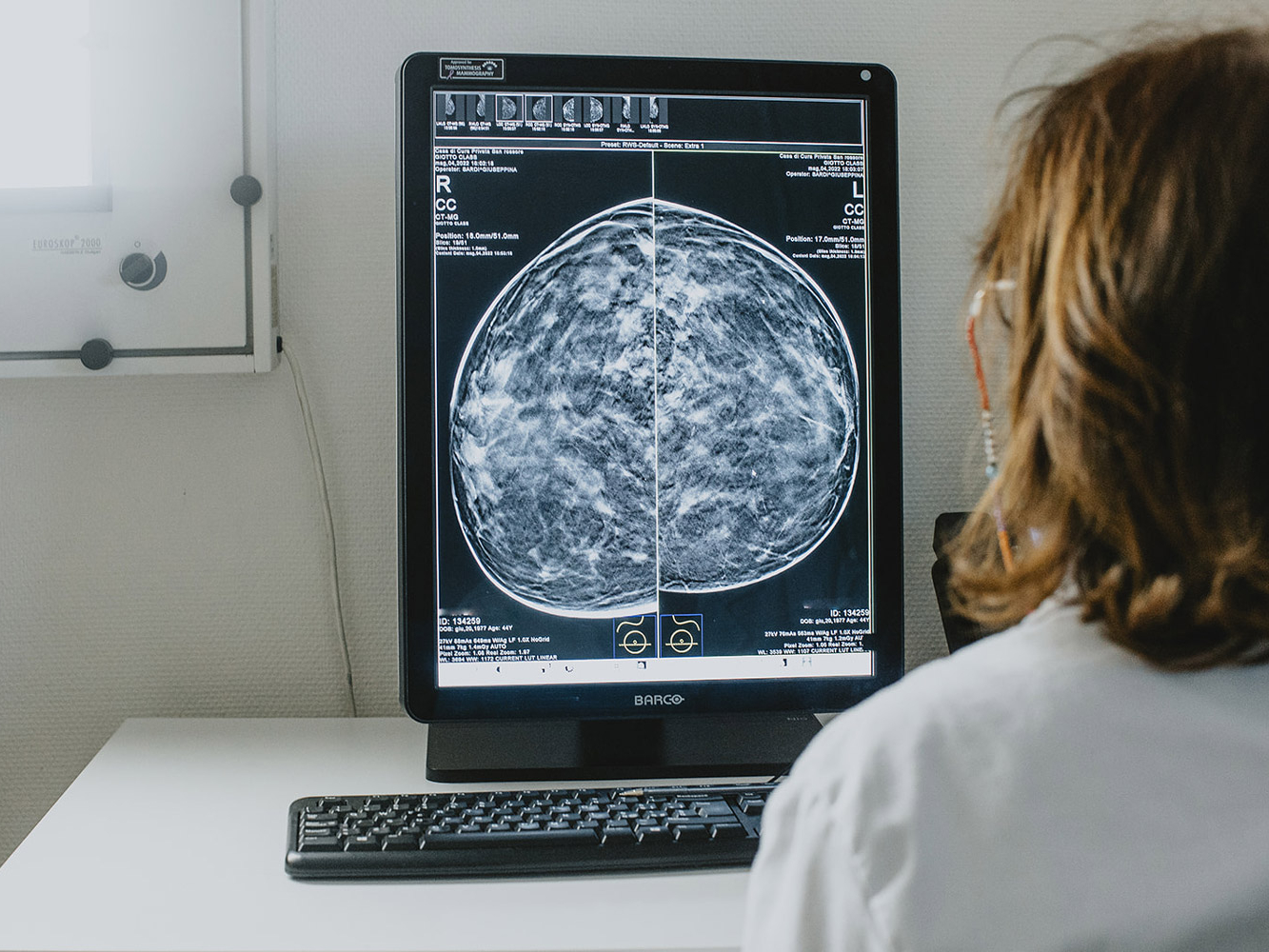
The radiologist makes the diagnosis with the support of the most innovative instrumentation: 3D mammography, ultrasound and MRI. The diagnosis is supported by a breast biopsy.
The pathologist will provide further information on the type of neoplasm, thus completing the diagnosis.
The breast surgeon and reconstructive plastic surgeon will discuss treatment options with the patient. Indications for partial or total mastectomy and sentinel lymph node biopsy will be screened with the breast surgeon. The Breast Unit’s oncoplastic approach to breast cancer treatment allows the use of innovative reconstructive techniques that are proposed by the plastic surgeon. Lymphoscintigraphy to search for the sentinel lymph node, which will be removed and biopsied during surgery, is performed by the nuclear physician.
The anesthesiologist is another key figure on the surgical team, as patient safety is always the priority at the San Rossore Breast Unit.
During convalescence, the patient is cared for by a dedicated group of nurses, and after surgery she is supported by the physical therapist with rehabilitation therapies. The patient is also given the opportunity to meet with the nutritionist before being discharged.
Once the diagnosis is completed with the results of surgery, the patient will be informed by the Breast Unit team about the indications, timing, and possible side effects of any additional adjuvant therapies proposed by the oncologist for chemotherapy and hormone therapy and by the radiation oncologist for radiation therapy, in accordance with treatment protocols.
Breast radiodiagnostics
Dr. Anna Cilotti
Dr. Carolina Marini
Dr. Barbara Ginanni
Reconstructive and Aesthetic Plastic Surgery
Dr. Claudio Calabrese
Dr. Antonella Puddu
Oncology
Dr. Monica Lencioni
Radiotherapy
Dr. Maria Grazia Fabrini
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarifications or other Info please fill out the form below, you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.
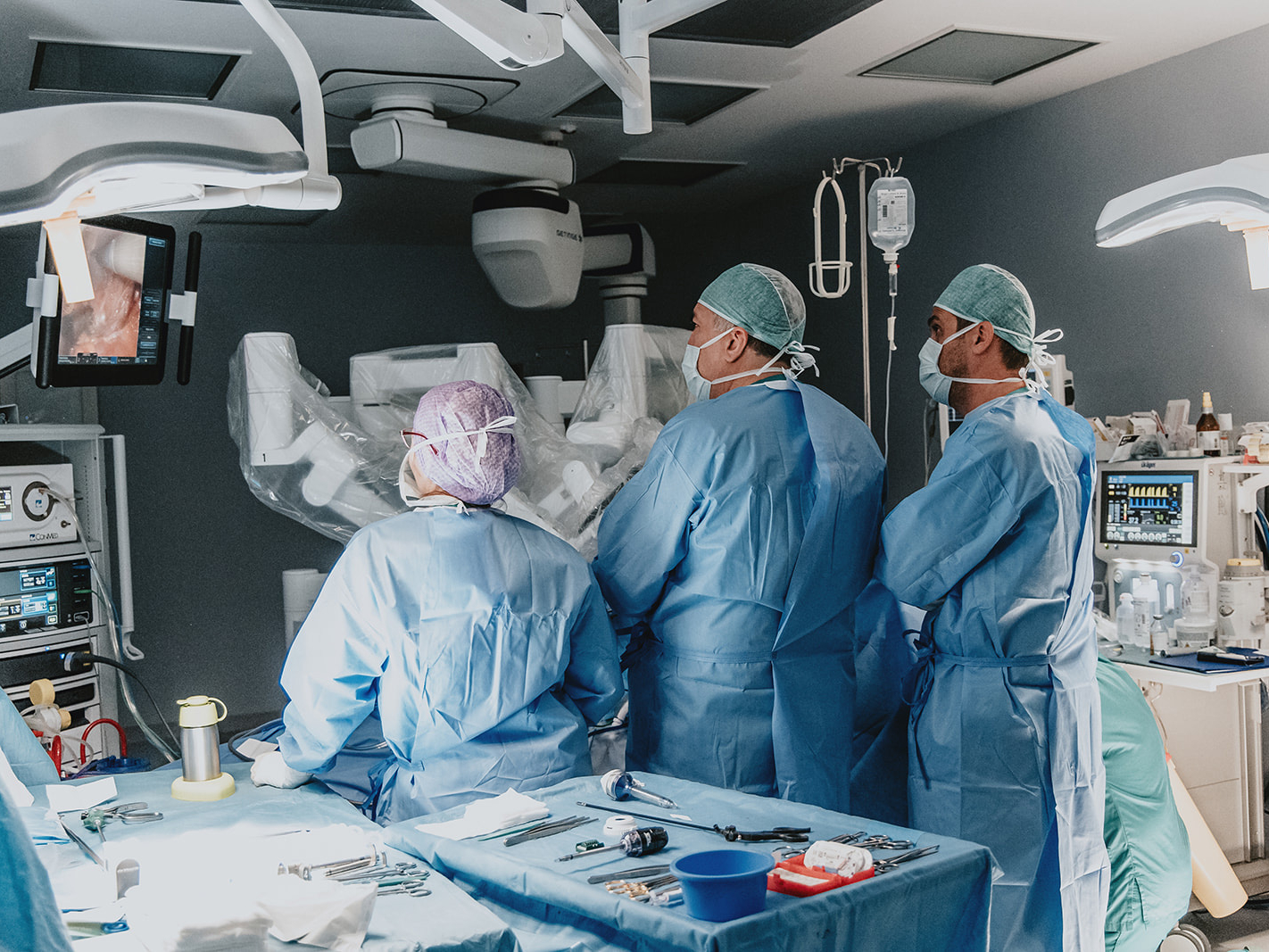
Center for Robotic Surgery
Center for Robotic Surgery
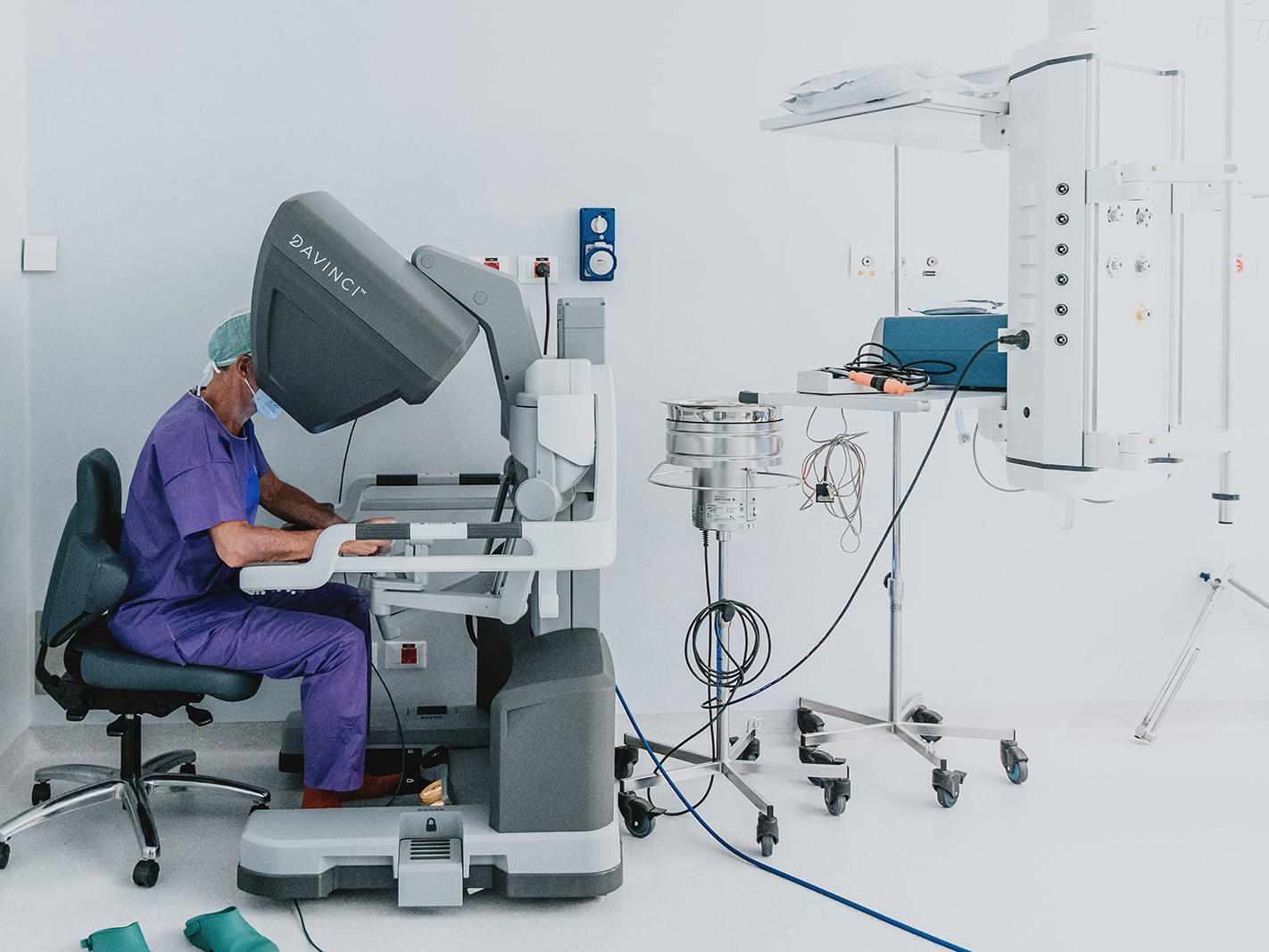
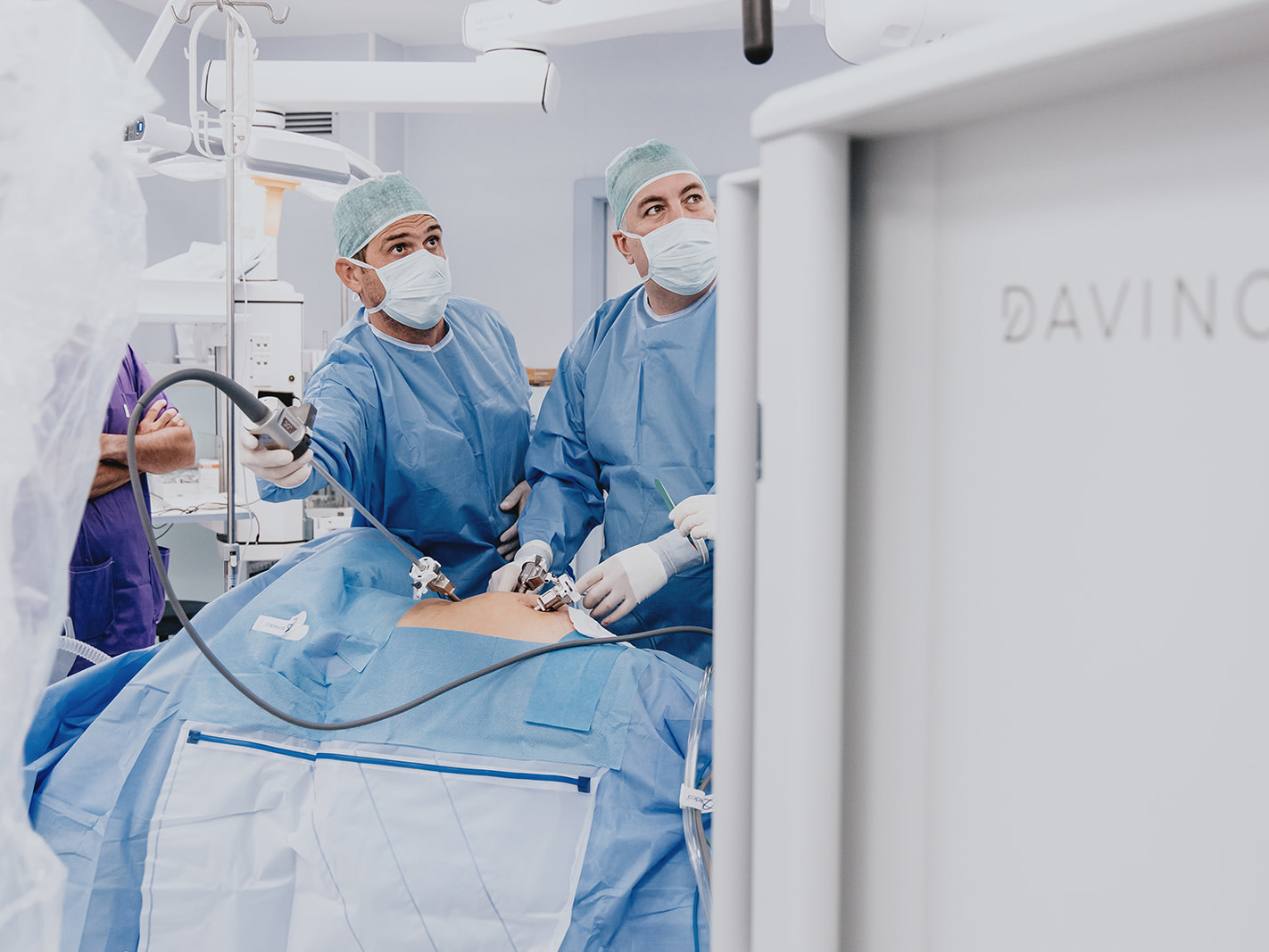
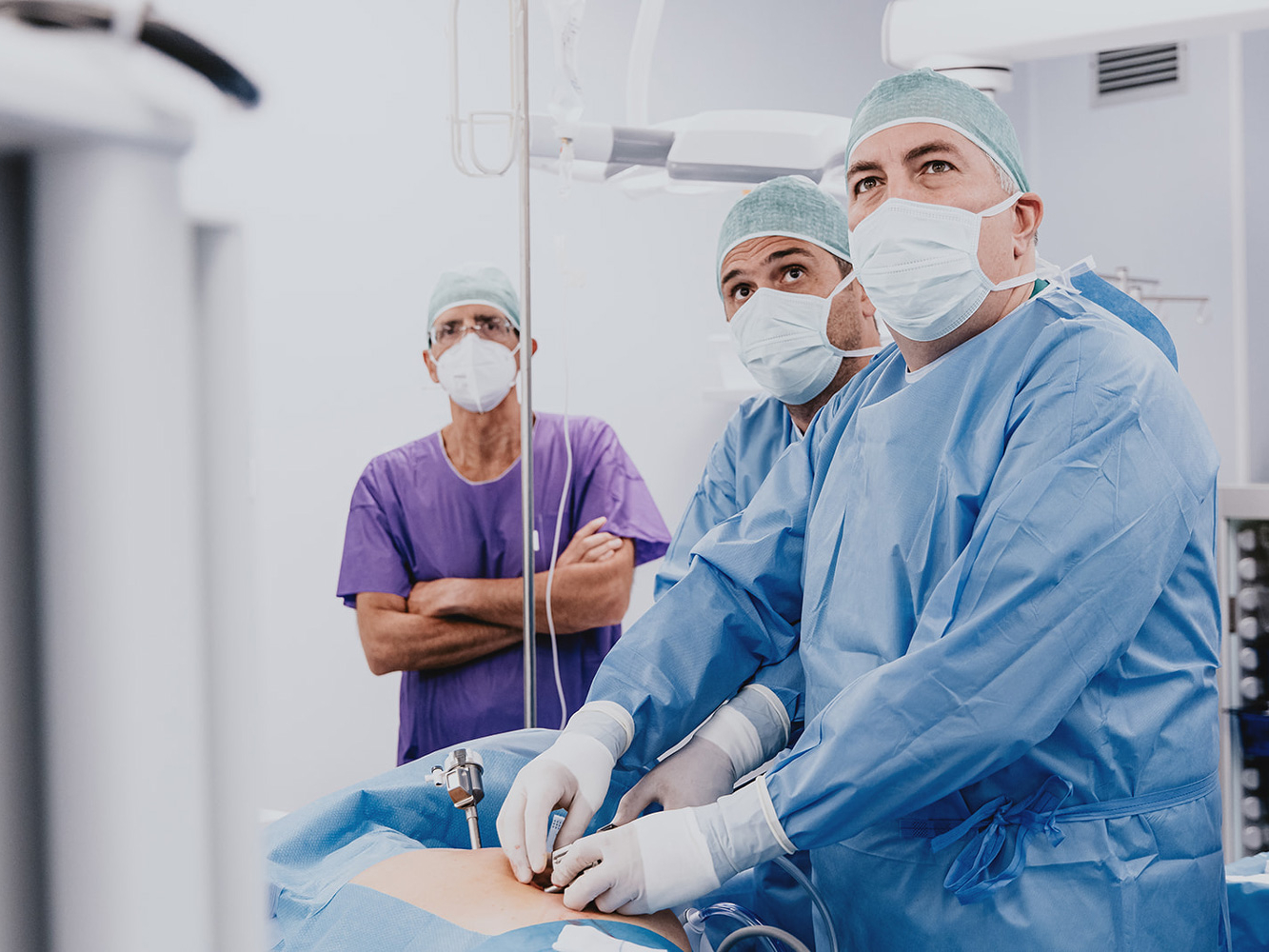
The Da Vinci robotic system, the most advanced robotic system for minimally invasive surgery, is available at Casa di Cura San Rossore.
Robotic surgery represents in the surgical field an increasingly minimally invasive approach to the patient, with benefits in postoperative treatment and a much shorter hospital stay.
Its technical features mean that the Da Vinci robot has a variety of applications, from urology to gynecology to general surgery.
Surgery performed with the Da Vinci Robot allows three-dimensional vision, millimeter precision in sutures, and 360-degree articulation of instruments not possible for the human hand. The surgeon does not operate with his or her own hands but by operating a robot remotely: sitting at a computerized console located inside the operating room, the computerized system transforms the movement of the hands into impulses that are conveyed to the robotic arms.
The da Vinci platform is the only robotic system that:
- It translates the surgeon’s movements intuitively
- It allows a true 3D view of the surgical field. The surgeon is literally “immersed,” without the aid of glasses or other equipment, inside the patient’s body.
- It allows intervention through single-site technology with single access through the umbilicus.
Da Vinci robotic surgery is applied to the following specialties:
- Urology
- General surgery
- Gynecologic oncology
- Thoracic Surgery
- Cardiac Surgery
- Pediatric urology
- Benign gynecology
- Otolaryngology
- Transplantation surgery
The main clinical benefits:
- Oncological radicality, then complete removal of the tumor mass
- Easy access to difficult anatomies
- Excellent visualization of anatomical findings
- More detailed visualization of cleavage plans
- Greater precision in the demolition procedure
- Greater reconstructive accuracy
- Ability to configure surgical motion accuracy (scales possible 1.5:1; 2:1; 3:1)
- Elimination of physiological tremor
- Less operative time compared with laparoscopy
Benefits to the patient:
- Small incisions with better aesthetic results
- Less need for transfusions
- Less postoperative pain
- Reduced hospitalization times, which in many cases are even halved
- Faster resumption of normal activity
Robotic Hepatobiliary Surgery
Dr. Emanuele Balzano
Urological Robotic Surgery
Dr. Massimo Cecchi
Dr. Filippo Menchini Fabris
Gynecologic Robotic Surgery
Dr. Vito Cela
Oncologic Robotic Surgery
Dr. Giuseppe Spinoglio
Proctologic Robotic Surgery
Dr. Alessandro Sturiale
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarifications or other Info please fill out the form below, you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.
Fibromyalgia Center
Fibromyalgia Center
Casa di Cura San Rossore offers a diagnostic and therapeutic pathway for patients with fibromyalgia and/or chronic fatigue, making use of the expertise of Dr. Laura Bazzichi (Rheumatologist) and Prof. Dr. Ciro Conversano (psychotherapist), who have been dealing with chronic pain with a multidisciplinary strategy for over 20 years.

Fibromyalgia, specifically, is a rheumatic disease classified as a chronic pain syndrome of unknown etiology (it affects more than 3% of the population). It is characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, the presence of precise algogenic points (Tender Points TPs) and a variety of accompanying dysfunctional symptoms, among which are:
Asthenia
Sleep alterations
Muscle aches and pains
Fibro-fog
Multidisciplinary therapy is the treatment strategy approved by the most accredited guidelines. Many of these patients undergo unnecessary examinations by turning to a wide variety of specialists to get the diagnosis and a guideline. In addition, many symptoms among those listed above are part of other diseases such as, for example, Long-Covid.
Our pathway follows the patient step by step, from useful blood tests, psychological and psychotherapeutic help programs, physiotherapy, to guidance on alternative and complementary therapies. Each stage of the multidisciplinary pathway involves the action of one or more specialists who may be beneficial to the individual patient and who will be selected and identified during the Rheumatology evaluation.
Hematochemical examinations
Psychological/psychiatric evaluationHematochemical examinations
Adapted physical therapy
Nutrition education
At the end of the diagnostic-therapeutic pathway, the rheumatologist will re-evaluate the patient with a brief visit, (including delayed) to set the follow-up schedule agreed upon with other specialists.
Rheumatology
Dr. Laura Bazzichi
Psychology
Dr. Ciro Conversano
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarifications or other Info please fill out the form below, you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.
Eating Disorders Center
Eating Disorders Center
For many years, the Center for the Treatment and Care of Eating Disorders has been operating at the Casa di Cura San Rossore.
Our Center consists of a team of specialized professionals (physician, psychiatrist, dietitian, psychologist) for an advanced approach that, depending on the need, allows different treatment modalities and pathways.
Eating Behavior Disorders or Disorders of Eating and Nutrition (DAN) are complex disorders characterized by psychological distress manifested by altered eating behaviors and habits related to an excessive preoccupation with weight and body shape.
Major eating disorders-anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, Binge Eating Disorder (BED) and eating disorders not otherwise specified-are one of the most common health problems among young people in our country, with a higher prevalence in the female gender.
– Anorexia nervosa
– Bulimia nervosa
– Uncontrolled Eating Disorder (Binge-Eating Disorder, BED)
– Nutrition or Eating Disorders not otherwise specified (e.g. subthreshold forms of Anorexia and Bulimia, Night Eating Syndrome, …)
– Orthorexia, Reverse Anorexia or Vigorexia
For these diseases, national and international guidelines indicate the need for diagnosis and treatment activities to be carried out in integrated multidisciplinary teams of specialists with specific training and experience in clinical settings.
The integrated multidisciplinary pathway for the treatment of Eating Disorders, based on psychotherapy, psycho-nutritional rehabilitation interventions, medical management and, if necessary, pharmacological interventions, also includes family support, family therapy, assisted meals, Food Familiarization Training (TFC), therapeutic group pathways.
Anorexia Nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is characterized by food restriction, underweight (more or less severe), intense fear of gaining weight, and body image disturbance; one of the most serious aspects is denial of the disease and resistance to therapeutic treatment.
In the general population older than 18 years of age and female, lifetime prevalence rates of 0.9% are estimated for anorexia nervosa; the incidence of anorexia nervosa is estimated to be at least 8 new cases per 100,000 women in a year, with increasingly early onset and late diagnosis. In studies of clinical populations, males account for 5% to 10% of anorexia nervosa cases.
Adolescence is the most frequent age of onset, and the disorder manifests progressively with reduction in daily caloric intake (iron diet) and through manifestations such as digestive disturbances, selectivity about food, reduced appetite, and excessive and obsessive use of physical activity. This leads to a more or less pronounced drop in body weight, sometimes reaching life-threatening levels and accentuating the psychopathological picture resulting from malnutrition (depressive symptoms, social withdrawal, irritability, preoccupation with weight, increased control over food…).
Hostility is initially directed mainly toward one’s own body, and food becomes an object of special attention and cooking a real hobby cultivated mainly for others; every meal turns into a time of great difficulty and battleground for the family, sometimes involving extreme behavior such as hiding or throwing away food.
While primarily psychiatric disorders, eating disorders often produce even serious physical complications secondary to malnutrition and/or improper behaviors enacted to gain control over weight and body shape. People with anorexia nervosa, in particular, have a mortality rate between 5 and 10 times higher than that of healthy people of the same age and sex, which is why it is identified by the O.M.S., worldwide, as the second leading cause of death among adolescents.
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa is characterized by recurrent episodes of binge eating followed by inappropriate compensatory behaviors aimed at avoiding weight gain (such as self-induced vomiting, improper use of laxatives or enemas, improper use of diuretics, prolonged fasting, or excessive exercise); there is present as in other eating disorders intense fear of gaining weight with excessive distorted assessment of weight and body shape, often associated low self-esteem.
In the general population older than 18 years and female, lifetime prevalence rates of 1.5% are estimated for bulimia nervosa. The incidence of bulimia nervosa is estimated to be at least 12 new cases per 100,000 women in a year. In studies of clinical populations, males account for between 10% and 15% of bulimia nervosa cases. Compared to Anorexia, episodes of binge eating are present, reinforced by food restriction and dieting, stress, or negative emotions. Loss of control is followed by a strong sense of guilt; vomiting and other compensation techniques are strategies, albeit dysfunctional, to manage body weight, control one’s life, and relieve stress and anxiety.
The possibility of the so-called “bulimic veering,” or the transition from anorexia to bulimia, is common, reinforced precisely by the biological drive to need food due to protracted food restriction and underweight.
Uncontrolled Eating Disorder or Binge-EatingDisorder (BED)
People suffering from Uncontrolled Eating Disorder present recurrent episodes of binge eating, without the use of compensatory behaviors.
In the general population older than 18 years and female, lifetime prevalence rates of 3.5 percent are estimated for BED. In studies conducted in clinical populations, males between 30% and 40% of BED cases.
Binge eating episodes are associated with at least three of the following characteristics:
– eat much faster than normal
– Eat until you feel unpleasantly full
– Eating large amounts of food when one does not feel physically hungry
– eating alone because you feel embarrassed by the amount of food you are eating
– feeling disgusted with themselves, depressed or very guilty after binge
– Marked discomfort with episodes of binge
The disorder is often accompanied by overweight or obesity and may be associated with medical complications related to overweight complications such as metabolic syndrome or other conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. A considerable percentage of people referred to bariatric surgery pathways suffer from this disorder.
Individuals suffering from Uncontrolled Eating Disorder often have high comorbidity with mood disorders, anxiety and depression.
Avoidant restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID)
Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) is a Nutrition and Eating Disorder more typical of children and prepubertal age (with greater frequency in the male sex than the other DANs). It manifests itself through persistent inability to meet appropriate nutritional needs resulting in weight loss and growth alterations; a medical-nutritional picture overlapping with that of Anorexia Nervosa can be realized.
Altered eating behavior can be characterized by:
– Lack of interest in food,
– Avoidance based on sensory characteristics of food (e.g., color, shape, texture…)
– Concern related to possible negative consequences of eating (e.g., choking or vomiting…).
Unlike other eating disorders such as Anorexia Nervosa, a desire to lose weight and significant concerns about body image are generally not detected.
Other Nutrition and Feeding Disorders
In addition to ARFID, there are rarer and generally more frequent disorders in childhood:
– Pica, characterized by persistent ingestion of substances without food content, inedible
– Rumination disorder, characterized by repeated regurgitation of food, which may be regurgitated, swallowed or spit out, in the absence of organic causes.
Finally, there are multiple clinical pictures that are mixed or in which one of the criteria is missing in order to make the diagnosis of a main form of eating disorder.
These clinical pictures go under the
diagnostic designation of otherwise specified Nutrition and Eating Disorders (e.g., atypical anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa, nocturnal feeding…) or without any other specification, but even with this definition it is not excluded that serious and urgent clinical situations may occur.
It consists of an initial medical examination by the head of the Center during which the patient’s medical history, request and expectations are collected, followed by a few meetings by the professionals of the team (dietitian/nutritionist, psychologist/psychotherapist, psychiatrist/NPI) to complete the diagnostic assessment and formulate a proposed treatment path.
Laboratory (e.g., blood chemistry tests, hormone assays, …) and instrumental (e.g., Indirect Calorimetry, BIA, Metabolic Holter, MOC, Abdomen Echo, sleep-wake rhythm assessment …) investigations are also performed depending on the clinical condition.
At the end of the assessment phase, the treatment plan will be shared and goals and timing of the treatment course will be defined together with the patient.
It is defined on the basis of the diagnosis made at the Assessment/Assessment stage, is highly personalized and focused on the specific clinical needs and problems of each subject, with variable duration depending on the clinical condition and with the possibility of structuring treatment paths with an intensive outpatient and/or semi-residential level of care.
Integrated multidisciplinary outpatient treatment includes individual psychotherapy interviews, nutritional visits with the dietitian, medical and psychiatric monitoring.
In the case of intensive or intensive/semi-residential outpatient treatment in addition to the above, it is possible to customize the course with mealtime assistance, TFC (Food Familiarization Training) or home/family-assisted meals, psycho-education course according to the Mausley method for family members, parenting support, family therapy, treatment of Body Image Disorder and other specific proposals according to the needs that emerged during assessment.
The treatment course, moreover, provide for periodic reevaluations and possible modifications of the project over time. At each stage, the person is at the center with a collaborative approach and flexibly uses therapeutic strategies and interventions, enhancing the resources of the patient and their loved ones.
The approach, with solid theoretical foundations and in line with National and International guidelines, is not standardized and based on a single model in order to enable the team of professionals, with different educational backgrounds, to activate the most effective tools for the person.
Medical area reference specialists
Dr. Giovanni Gravina – Head of the Eating Disorders Center, a physician specializing in Endocrinology and specially trained and experienced in the treatment of DAN
Dr. Grazia Nebbiai – Physician specializing in Endocrinology
Nutrition area reference specialists
Dr. Carla Piccione – Responsible Dietitian
Dr. Camilla Casagrande – Dietitian
Dr. Martina Francesconi – Biologist Nutritionist
Dr. Francesca Cipolli – Biologist Nutritionist
Dr. Guido Guidotti – Dietitian
Dr. Alessia Benedetti – Dietitian
Referral specialists psychological area
Dr. Ilaria Genovesi – Psychologist, Psychotherapist Responsible
Dr. Lucia Ricci – Psychologist, Psychotherapistav
Dr. Ramona Biasci – Psychologist, Psychotherapist
Dr. Irene Mazzei – Psychologist, Psychotherapist
Dr. Sara Pucci – Psychologist, Psychotherapist
Referral specialists psychiatric area
Dr. Adolfo Bandettini Di Poggio – Psychiatrist
Dr. Luca Maggi – Psychiatrist
Dr. Chiara Pfanner – Psychiatrist
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarification or other info call +39 050 586 428 (secretary) or fill out the form below, and you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.
Clinical Nutrition Center and Obesity
CLINICAL NUTRITION CENTER AND OBESITY
Adequate nutrition is fundamental to health and in the treatment of many diseases; it guarantees an improvement in nutritional status, well-being and quality of life.
The Clinical Nutrition Centre offers patients effective answers through customised nutritional paths agreed with specialists based on the clinical picture, laboratory and instrumental tests, history and lifestyle/dietary habits.
The Centre employs qualified professionals specialised in every nutritional field and state-of-the-art instruments for the assessment of body composition and individual energy needs (BIA, metabolic Holter, indirect calorimetry).
- Areas of intervention
- Obesity and body weight management
- Metabolic pathologies
- Wellness, relationship with food and the body
- Women’s area
- Nutrition and Sport
Obesity is a complex condition, characterized by an accumulation of adipose tissue, often to such an extent that it compromises an individual’s psycho-physical health and worsens his or her quality of life. The causes are multiple and heterogeneous; they may relate to the person’s life and dietary history, psychological aspect, genetic factors, metabolic aspects, stress level, lifestyle and eating habits.
Body weight management’ refers to a pathway aimed at achieving a healthy and appropriate lifestyle and diet, and a balanced relationship with one’s body and food.
The pathway can make use of various strategies useful for achieving the desired goals agreed upon with the person (and possible referral and collaboration with professionals specialised in bariatric surgery and the placement of reversible mechanical devices for weight loss, e.g. the Allurion gastric balloon pathway).
- nutritional counselling
- psychological counselling
- specific diet protocols
- anti-obesity drugs
Metabolic pathologies
Nutrition plays an important role in the body’s well-being, especially in certain clinical conditions for which an adequate and balanced diet is part of the therapeutic treatment.
The Centre provides medical-nutritional counselling for metabolic diseases and/or clinical conditions such as:
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Renal Failure
- Coeliac disease and malabsorption
- Food intolerances and allergies
- Dyslipidemias (hypercholesterolaemia, hypertriglyceridaemia,…)
- Arterial hypertension
- Hyperuricaemia
- Oncological pathologies
- Overweight and obesity related to metabolic diseases
Well-being, relationship with food and the body
The culture of dieting, the ideal of thinness, the vast amount of information about food and its specific nutritional properties have increasingly distanced us from a healthy relationship with food, with the body and from listening to the signals it sends us, which are fundamental, instead, for developing our ability to self-regulate with food while respecting the body.
The Centre provides courses in:
- Nutrition education
- Nutritional counselling
- Intuitive Eating
- Mindful Eating
Women’s Area
Women at different stages of life, from adolescence to pregnancy to menopause, are subject to physiological changes or the onset of special clinical conditions for which nutritional needs may change or require support.
Our Centre provides medical-nutritional counselling for special conditions such as:
- Growth, menstrual cycle
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- PCOS
- Medically Assisted Procreation (PMA)
- Menopause
Nutrition and Sport
Physical activity is part of an individual’s appropriate and healthy lifestyle to promote their development and maintain good health, both in the short and long term.
An adequate, varied and balanced diet is of fundamental importance to meet the special energy and nutritional needs of amateur and elite athletes.
Our Centre provides medical-nutritional advice in relation to the sporting activity performed, in synergy with the professionals at San Rossore Sport Village.
Treatment at our Centre involves a two-stage pathway: an initial assessment and evaluation phase and a subsequent therapy phase.
Diagnostic /Assessment pathway:
Consists of an initial medical examination by the Centre manager, during which the patient’s clinical history, request and expectations are collected in order to assess/agree together on the objectives and the most appropriate course to be taken.
Subsequently, 1-2 nutritional visits are agreed upon, with one of the Centre’s specialised dieticians/nutritionists, in order to complete the nutritional picture and structure a customised medical-nutritional pathway specific to the patient’s needs and requirements.
Depending on the clinical condition, laboratory (e.g. haematochemical examinations, hormone dosages, etc.) and instrumental investigations (e.g. Indirect Calorimetry, BIA, Metabolic Holter, MOC, Abdominal Echo, sleep-wake rhythm assessment) will be indicated.
At the end of the assessment phase, the treatment plan will be shared, and the objectives and timing of the treatment course will be defined together with the patient.
Treatment pathway:
Defined on the basis of the diagnosis made during the assessment/assessment phase, it is customised and focused on the specific needs and clinical problems of each individual. The path is proposed and agreed upon with the person, evaluating the most useful therapeutic strategies, including the use of drugs and/or supplements.
The Centre avails itself of the collaboration of specialists at the Treatment Centre according to the person’s needs (e.g. specialists in gynaecology, cardiology, physiotherapy, etc.).
The treatment pathway also provides for periodic re-evaluations and possible modifications of the project over time.
Bioimpedance analysis
A non-invasive examination performed with the BIA AKERN 101 instrument to assess body composition (hydro-electrolyte and nutritional balance). It enables the assessment of specific indices (e.g. lean mass, fat mass, active cell mass and water compartments) and can be used in various physiological and pathological clinical conditions, such as in states of malnutrition, weight loss, pregnancy and in the elderly. It is a Gold Standard examination for Sports Nutrition and Environment, Rehabilitation, and Sports Medicine. An analysis with BIA also allows, if repeated over time, a monitoring of the course of therapy and/or physical/sports training.
Indirect calorimetry
A non-invasive examination carried out with the FITMATE COSMED instrument, which makes it possible to measure real/current energy expenditure at rest by measuring oxygen consumption. This type of examination estimates, with greater precision than theoretical formulas, the basal metabolism, i.e. the energy required for vital functions at rest; a correct evaluation of this parameter thus allows the definition of personalised and targeted plans for weight management and other nutritional objectives.
SleepActa-DORMI
It is a non-invasive examination performed with the DORMI partners SLEEPACTA instrument for sleep and lifestyle assessment.
“DORMI is a wearable device (watch bracelet) that monitors sleep disorders (sleep holter), non-invasive and extremely accurate. It is a technologically advanced instrument that, through the accurate monitoring of the sleep-wake cycle and certain parameters (e.g. heart rate, movement), allows an accurate diagnosis of the quantity and quality of sleep. The analysis of the recorded data is aimed at providing a representation of sleep patterns and allows an estimation of the risk of developing possible pathologies.
Scientific evidence has demonstrated the correlation between poor quality and quantity of sleep and weight gain; therefore, with synergetic work between different specialised professionals, it is possible to monitor the state of health and improve it through a highly customised pathway.
Referring Specialists Medical Area
Dr. Giovanni Gravina (Head of the Centre) – Specialist in Endocrinology and specially trained and experienced in the treatment of DAN.
Dr. Grazia Nebbiai (Medical doctor specialising in Endocrinology)
Dr. Cristina Ferrauto (Doctor)
Dr. Dalila Fiorino (Doctor)
Nutrition area reference specialists
Dr. Carla Piccione (Dietician in charge)
Dr. Camilla Casagrande (Dietician)
Dr. Martina Francesconi (Biologist Nutritionist)
Dr. Francesca Cipolli (Biologist Nutritionist)
Dr. Alessia Benedetti (Dietitian)
Dr. Guido Guidotti (Dietitian)
Dr. Ilaria De Gioia (Biologist Nutritionist)
Psychological area reference specialists
Dr. Ilaria Genovesi (Psychologist, Psychotherapist in charge)
Dr Lucia Ricci (Psychologist, Psychotherapist)
Dr. Ramona Biasci (Psychologist, Psychotherapist)
Dr. Irene Mazzei (Psychologist, Psychotherapist)
Dr. Sara Pucci (Psychologist, Psychotherapist)
INFO POINT
Contact us
Per domande, chiarimenti o altre info chiama il numero +39 050 586 428 (segreteria) o compila il form sottostante, sarai ricontattato al più presto dal nostro personale addetto.
Pain Center
Pain Center
At Casa di Cura San Rossore is the Pain Unit and Palliative Care, the center specializing in the treatment and care of chronic pain.

The idea of the Pain Unit stems from a simple yet sad fact: in Italy, about thirteen million people are affected by chronic pain, and of these, 45% have been living for more than 6 months without having found a solution to the problem, just as 17% have not found lasting remedies for more than 5 years. The Pain Unit and Palliative Care, therefore, aims to improve the living conditions of people with and without chronic oncological pain.
Pain therapy consists of the interventions useful in identifying and applying therapies to eliminate and control pain, regardless of the cause. It includes not only drug therapies, but also surgical, instrumental, psychological and rehabilitation therapies, variously integrated with each other.
With the Pain Unit, the Casa di Cura San Rossore wants to create a comprehensive and innovative therapeutic pathway that brings together the multidisciplinarity needed for patient care in a single health center.
L’approccio multidisciplinare, infatti, rende possibile fornire simultaneamente consulti e attività che, di norma, vengono erogati in diverse strutture e in tempi differenti. Specifically, the center aims to improve the living conditions of people with chronic pain, reducing the degree of disability and promoting their reintegration into social and work environments.
The Pain Unit provides a collaborative form of patient assessment and care by specialists in:
- Anesthesia and resuscitation
- Neurosurgery
- Orthopedics
- Neurology
- Physiatry
- Oncology
- Psychology
- Physiotherapy
- Nutrition
After an initial diagnostic evaluation, in the most complex cases, the patient will subsequently be able to access an inpatient day hospital in which he or she will have the opportunity to interact with the previously indicated specialists.
Upon completion of the assessment, the Pain Unit Coordinator will deliver a clinical report along with a proposed treatment plan for the patient. Once accepted, the patient’s intended course of treatment is activated.
Neurosurgery
Dr. Matteo Capozza
Physiotherapy
Dr. Simone Casarosa
Dr. Giovanni Santarelli
Neurology
Dr. Ferdinando Sartucci
Pain Therapy
Dr. Giuliano De Carolis
Endocrinology
Dr. Giovanni Gravina
Oncology
Dr. Monica Lencioni
Psychiatry
Dr. Chiara Pfanner
INFO POINT
REQUEST INFORMATION
For questions, clarifications or other Info please fill out the form below, you will be contacted by our dedicated staff as soon as possible.